Relationship-based access control
Throughout this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the implementation of basic relationship-based access control model in Aidbox. We’ll assume you have Aidbox up & running already locally or in cloud.
Where to get help:
If you’re having trouble going through this tutorial, please head over to our Aidbox community chat.
In this tutorial we will
- model authorization for our sample application called Research Study Repository
- implement that authorization model in Aidbox with AccessPolicy engine.
Authorization model
We will model access for an example application called Research study repository. The system is going to give researchers an access to research studies and related patient records.
Our security policy says:
_User has access to all studies they collaborate on and to all patient records within those studies._
Authorization model that best suits our task is relationship-based access control (ReBAC). It states that 'subject's permission to access a resource is defined by the presence of relationships between those subjects and resources'.
We will focus only on read access, expecting that all data is uploaded. We will upload prepared sample data later on implementation section.
But before we dive into defining authorization, let's discuss our data model and UI we are going to provide our users. Good data model and UI leads to easier authorization.
Data model & UI
The core entity of our application will be a research study. There is a ResearchStudy resource in FHIR, which describes 'a process where a researcher or organization plans and then executes a series of steps intended to increase the field of healthcare-related knowledge'.
ResearchStudy references to Group of patients invloved in the research with ResearchStudy.enrollment element. Patient record is represented by two resources Patient and Observation.
ResearchStudy doesn't have references to collaborators. So, we will introduce one and make a linkage with Aidbox User.
Data model of Research study repository application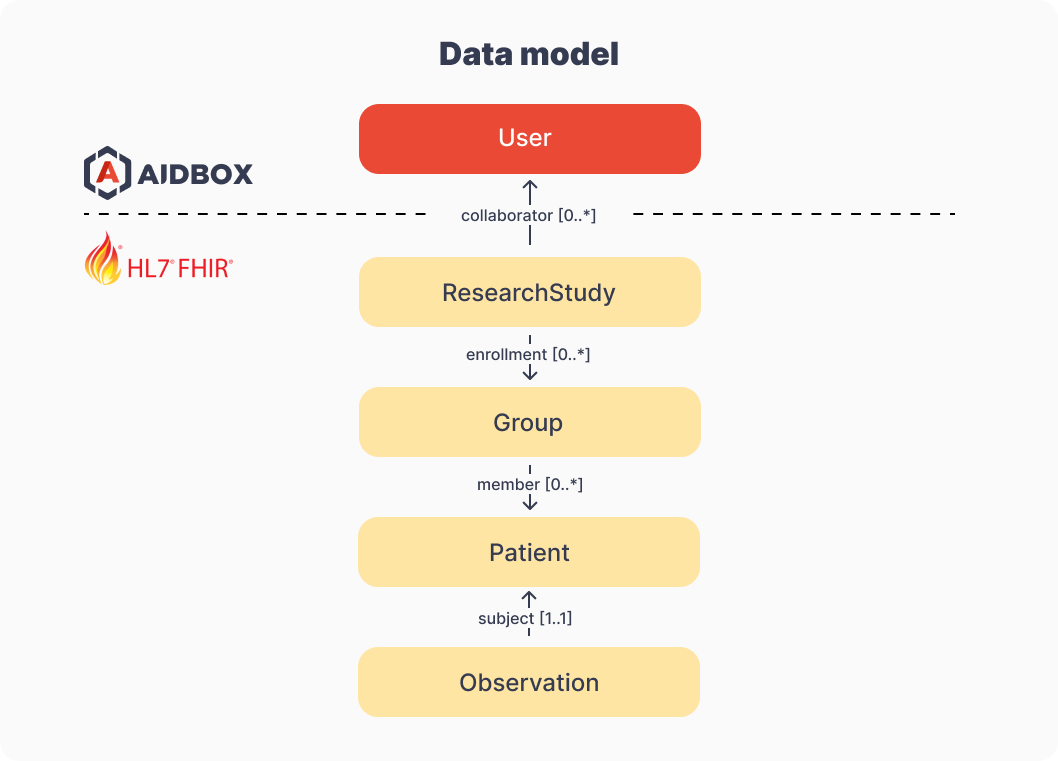
As ResearchStudy resource is a core of our model, it's reasonable to make the list of available studies a starting point on UI. So we may imagine user's flow within UI.
- Researcher enters the system and see the list of studies, they involved into as a collaborator.
- They can drill down to a study to see details and search over related patients and observations.
UI pages & FHIR requests for Research study repository application.png)
Once we defined our data model, UI pages and FHIR requests, we may start implementing this.
Implementation
As we mentioned earlier, FHIR ResearchStudy doesn't have references to collaborators. It's good to start with enabling this reference.
Add reference to collaborators
There are many ways you can customize your data model with Aidbox. We will do this by creating Entities & Attributes.
There is an HTTP request below for creating Attribute/ResearchStudy.collaborator. You can perform this request in Aidbox REST Console.
PUT /Attribute/ResearchStudy.collaborator
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
description: List of study collaborators
resource: {id: ResearchStudy, resourceType: Entity}
path: [collaborator]
type: {id: Reference, resourceType: Entity}
isCollection: true
refers: [User]
extensionUrl: urn:extension:researchStudyMemberIf you use zen profiles, Attribute resources will be disabled. Thus, you will need to define your attributes in zen.
Upload sample data
Aidbox is ready to store our data, and we prepared data samples, so we could test our access policies. You can use the request below to upload sample data.
PUT /
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
- {"id":"jane","resourceType":"User"}
- {"id":"janes-session","resourceType":"Session","user":{"id":"jane","resourceType":"User"},"access_token":"janes-access-token"}
- {"id":"oscar","resourceType":"User"}
- {"id":"oscars-session","resourceType":"Session","user":{"id":"oscar","resourceType":"User"},"access_token":"oscars-access-token"}
- {"id":"patient-1","resourceType":"Patient"}
- {"id":"patient-1-obs-1","resourceType":"Observation","subject":{"id":"patient-1","resourceType":"Patient"},"status":"final","code":{"coding":[{"system":"http://loinc.org","code":"718-7","display":"hemoglobin [mass/volume] in blood"}]}}
- {"id":"patient-2","resourceType":"Patient"}
- {"id":"patient-2-obs-1","resourceType":"Observation","subject":{"id":"patient-2","resourceType":"Patient"},"status":"final","code":{"coding":[{"system":"http://loinc.org","code":"718-7","display":"hemoglobin [mass/volume] in blood"}]}}
- {"id":"patient-3","resourceType":"Patient"}
- {"id":"patient-3-obs-1","resourceType":"Observation","subject":{"id":"patient-3","resourceType":"Patient"},"status":"final","code":{"coding":[{"system":"http://loinc.org","code":"718-7","display":"hemoglobin [mass/volume] in blood"}]}}
- {"id":"group-1","resourceType":"Group","actual":true,"type":"person","member":[{"entity":{"id":"patient-1","resourceType":"Patient"}},{"entity":{"id":"patient-2","resourceType":"Patient"}}]}
- {"id":"group-2","resourceType":"Group","actual":true,"type":"person","member":[{"entity":{"id":"patient-2","resourceType":"Patient"}},{"entity":{"id":"patient-3","resourceType":"Patient"}}]}
- {"id":"smoking-research","resourceType":"ResearchStudy","status":"active","enrollment":[{"id":"group-1","resourceType":"Group"}],"collaborator":[{"id":"jane","resourceType":"User"},{"id":"oscar","resourceType":"User"}]}
- {"id":"diet-research","resourceType":"ResearchStudy","status":"active","enrollment":[{"id":"group-2","resourceType":"Group"}],"collaborator":[{"id":"oscar","resourceType":"User"}]}The picture below, demonstrates the key data we uploaded. Jane has access to 'Smoking research', and both users have access to 'Diet research'.
Sample data for research study repository application.png)
Write access policies
Now, we are ready to define available enpoints and write AccessPolicy for them.
List of studies
The endpoint to fetch all user's research studies is
GET /ResearchStudy?collaborator=<user-id>FHIR doesn't have search parameter collaborator. Aidbox allows you to define one with SearchParameter.
PUT /SearchParameter/ResearchStudy.collaborator
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
name: collaborator
type: reference
resource: {id: ResearchStudy, resourceType: Entity}
expression:
- [collaborator]AccessPolicy:
PUT /AccessPolicy/user-can-search-their-research-studies
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
description: User can search for research studies, they collaborate on
engine: matcho
matcho:
request-method: get
uri: /ResearchStudy
params:
collaborator: .user.id
_with: nil?
_include: nil?
_revinclude: nil?
user:
id: present?Why did we explicitly exclude _include, _revinclude and _with parameters?
matcho engine compares incoming request with defined pattern, if the key is not specified in pattern, it will be ignore while checking. _include, _revinclude and _with parameters expands the list of returning data with related resources. As far we want to leave only ResearchStudy resources, we excluded them explicitly.
Read more on AccessPolicy best practicies guide.
Let's check it.
GET /ResearchStudy?collaborator=jane
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 200 OKGET /ResearchStudy
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 403 ForbiddenGET /ResearchStudy?collaborator=oscar
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 403 ForbiddenWe have secured endpoint for fetching list of studies. Note, that all search parameters for ResearchStudy is also available.
Read study details
The endpoint to fetch research study details is
GET /ResearchStudy/<research-study-id>It's not possible find out if current user is a collaborator on this study or not by only research study id . Fortunately, Aidbox AccessPolicy supports sql engine, which allows you to make your authorization decisions based on data you have.
PUT /AccessPolicy/user-can-read-their-research-study
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
description: User can research study, they collaborate on
engine: complex
and:
- engine: matcho
matcho:
request-method: get
uri: "#/ResearchStudy/.+"
user:
id: present?
- engine: sql
sql:
query: |
SELECT true
FROM "researchstudy"
WHERE
id = {{params.resource/id}}
and "researchstudy".resource @> jsonb_build_object('collaborator', jsonb_build_array(jsonb_build_object('id', {{user.id}}::text)))
limit 1
# 201 Created, 200 OKLet's check it.
GET /ResearchStudy/smoking-research
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 200 OKGET /ResearchStudy/diet-research
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 403 ForbiddenGET /ResearchStudy/diet-research
Authorization: Bearer oscars-access-token
# 200 OKWe have secured one more endpoint. There are only two left.
Search for patients
The endpoint to fetch all patients by group is
GET /Patient?_has:Group:member:_id=<group-id>You may have a lot of questions to this request.
- what does mean
_has:Group:member:_idand - where do we know group id if we don't have access to Group resource?
What does mean _has:Group:member:_id?
The _has parameter is a one of standard search parameters in FHIR, called reverse chaining. FHIR specification says:
The
_hasparameter provides limited support for reverse chaining - that is, selecting resources based on the properties of resources that refer to them...
The _has parameter always goes with modifiers, which specify the search parameter. Let's get back and read the request we have.
GET /Patient?_has:Group:member:_id=<group-id>This requests the server to return Patient resources, where the patient resource is referred to by at least one Group with id \
Where do we know group id, if we don't have access to Group resource?
Technically we don't need to have access to Group resource, we need only to know group id. And group id is available from ResearchStudy resource, we already have access to.
Thus, we may conclude the request is suitable for our needs. the AccessPolicy should check existence of ResearchStudy with that \
PUT /AccessPolicy/user-can-access-patient-related-research-study-group
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
engine: complex
and:
- engine: matcho
matcho:
request-method: get
uri: /Patient
params:
'_has:Group:member:_id': present?
_include: nil?
_revinclude: nil?
_with: nil?
user:
id: present?
- engine: sql
sql:
query: |
SELECT true
FROM "researchstudy"
WHERE "researchstudy".resource @>
jsonb_build_object('collaborator', jsonb_build_array(jsonb_build_object('id', {{user.id}}::text)),
'enrollment', jsonb_build_array(jsonb_build_object('id', {{params._has:Group:member:_id}}::text)))
limit 1Let's check it.
GET /Patient?_has:Group:member:_id=group-1
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 200 OKGET /Patient?_has:Group:member:_id=group-2
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 403 ForbiddenGET /Patient
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 403 ForbiddenGET /Patient?_has:Group:member:_id=group-2
Authorization: Bearer oscars-access-token
# 200 OKSearch for patient endpoint is secured. The only one is left.
Search for observations
The endpoint to fetch all observation by group is
GET /Observation?group=<group-id>There is no group search parameter for Observation in FHIR. And there is no way to define our parameter with SearchParameter resource.
To enable complex search parameters, Aidbox provides Search Resource resource. We will specify one for search Observations by group:
PUT /Search/Observation.group
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
name: group
resource: {id: Observation, resourceType: Entity}
where: '{{table}}.resource#>>''{subject,id}'' in (select member#>>''{entity,id}'' from "group", jsonb_array_elements(resource#>''{member}'') member where id = {{param}})'Chained-search & \_has search parameter in FHIR R5
FHIR R5 is going to introduce chained-search support for \_has parameter. So, our request would look like the following
GET /Observation?patient._has:Group:member:_id=<group-id>Aidbox is going to support it, once FHIR R5 is released.
The AccessPolicy will be very similar to previous one, we made for Patient search.
PUT /AccessPolicy/user-can-access-observation-related-research-study-group
Content-Type: text/yaml
Accept: text/yaml
engine: complex
and:
- engine: matcho
matcho:
request-method: get
uri: /Observation
params:
group: present?
_include: nil?
_revinclude: nil?
_with: nil?
user:
id: present?
- engine: sql
sql:
query: |
SELECT true
FROM "researchstudy"
WHERE "researchstudy".resource @>
jsonb_build_object('collaborator', jsonb_build_array(jsonb_build_object('id', {{user.id}}::text)),
'enrollment', jsonb_build_array(jsonb_build_object('id', {{params.group}}::text)))
limit 1Let's check it.
GET /Observation?group=group-1
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 200 OKGET /Observation?group=group-2
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 403 ForbiddenGET /Observation
Authorization: Bearer janes-access-token
# 403 ForbiddenGET /Observation?group=group-2
Authorization: Bearer oscars-access-token
# 200 OKSearch for observation endpoint is secured for now. All endpoints are secured.
That's it
Let's recap, what we have done. There was a security policy, which stated:
_User has access to all studies they collaborate on and to all patient records within those studies._
And we met this requirement using ReBAC authorization model. In order to achieve this we
- defined domain model resources, UI pages and FHIR endpoints for our application,
- and we developed access policies in Aidbox to secured the endpoints.
What's next
Writing access policies may be tricky some time, Aidbox has tooling to Debug access control.
Talk to a Health Samurai Engineer
If you'd like to learn more about using Aidbox or have any questions about this guide, connect with us on Telegram. We're happy to help.